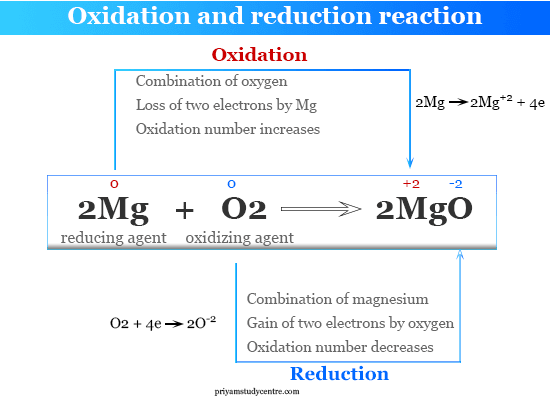
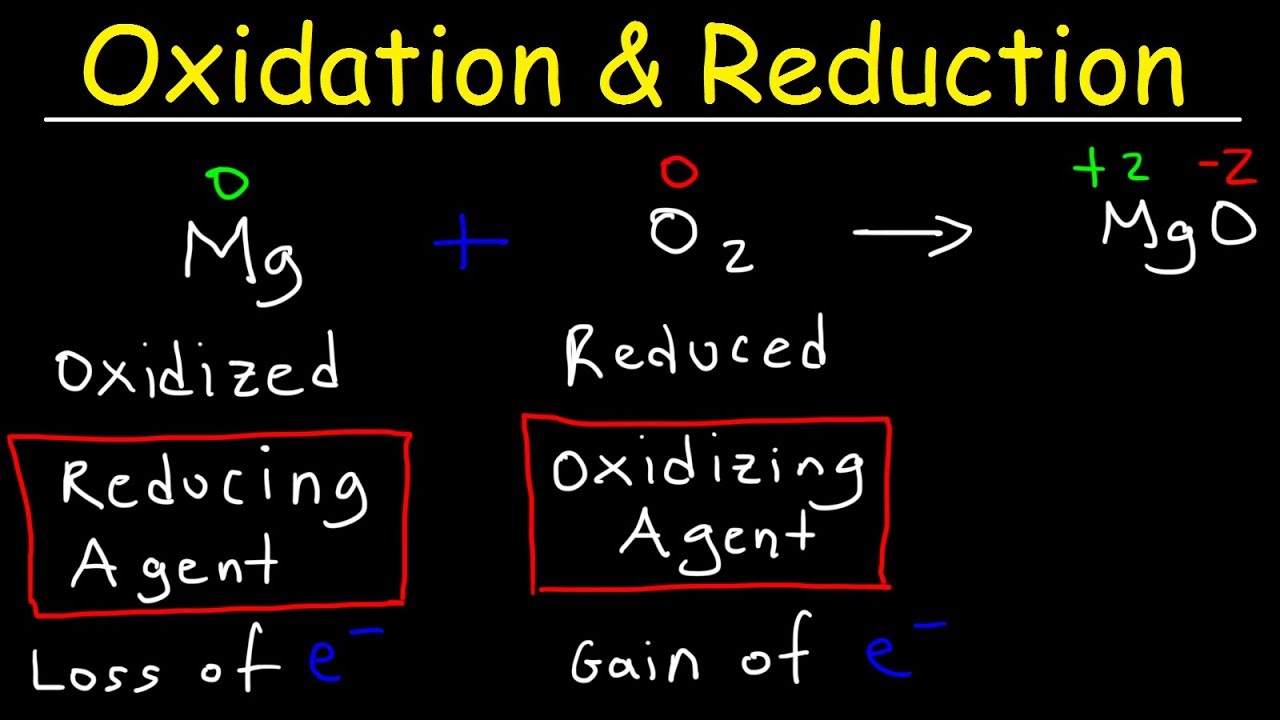
Magnesium oxygen magnesium oxide. When oxidized loses electrons it can cause reduction in the gain of electrons to remember this always think OILRIG.
Oxidation Reduction Reaction Definition Concept Examples
Rusting is an example of oxidation.

. It is also the loss of oxygen from a. Depending on the chemical reaction oxidation. Oxidation-Reduction Redox Reactions Reduction is the process of gaining one or more electrons.
A substance that gains electrons is said to be reduced. The opposite of oxidation is reduction. A reduction-oxidation or redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which reduction and oxidation occur at the same time.
We say that it has been reduced to copper. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction where the oxidation number of a molecule atom or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron. Reduction and oxidation occur simultaneously in a type of chemical reaction called a reduction-oxidation or redox reaction.
Oxidation is a chemical change that involves the transfer of electrons or oxygen among atoms. Oxidation-reduction or redox Any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a participating chemical species changes. During oxidation a substance gains oxygen.
In an oxidation-reduction or redox reaction one atom or compound will steal electrons from another atom or compound. In H 2 O its oxidation state is -2 and it has been reduced. Notice that oxygen is present in the reactant and both products.
The oxidation state of the molecule atom or ion gets increased during the oxidation process by the loss of electrons. 2 Na Cl2 2 NaCl. 2Mg O2 2MgO.
Oxidation Reduction Reaction Definition. What happens in a Oxidation-Reduction Redox Reaction. Chemists often treat the electrons as actual particles which to a 1st approx.
Specifically we see that oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons and reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons and we learned a handy acronym to help us remember this fact. Usually the change in oxidation number is associated with a gain or loss of electrons but there are some redox reactions eg covalent bonding that do not involve electron transfer. Oxidation is loss of electrons gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
Na Na. When rusting happens oxygen steals electrons from iron. In the equation the copperII oxide has lost its oxygen.
Addition of hydrogen or electrons or removal of oxygen is reduction and removal of hydrogen or electrons or addition of oxygen is oxidation. A change occurs in the number of electrons. Sodium atom is monovalent because it loses one electron and changes into the positive ve ion This process is known as the oxidation process Sodium atom is oxidized because it loses an electron and changes into ve ion Sodium atom is considered as a reducing agent because it loses gives an electron.
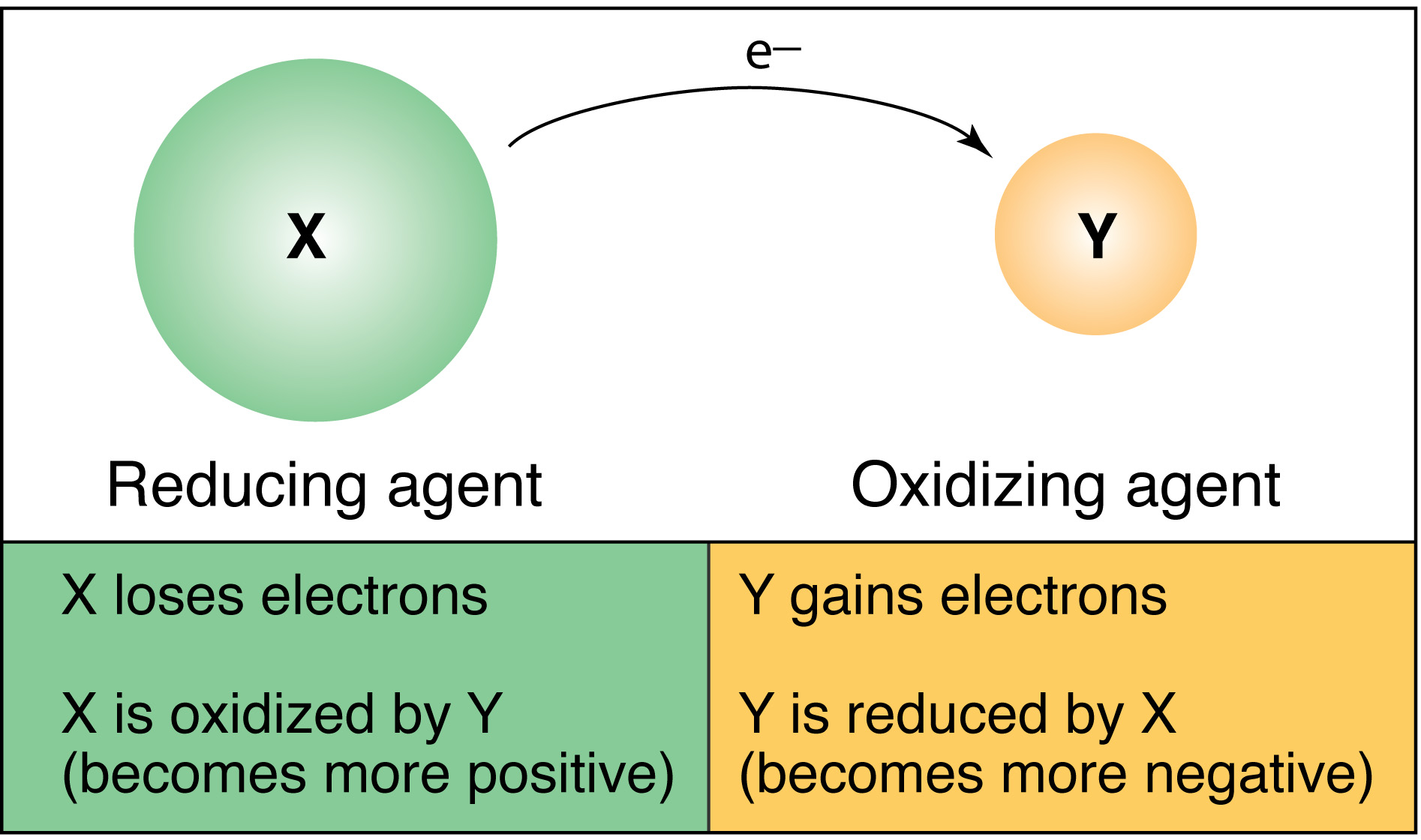
Oxidation can be defined as the process when an atom or an ion loses electrons. Electrons are transferred from one molecule or ion to another. Oxidation involves an increase in oxidation number while reduction involves a decrease in oxidation number.
Oxidation and reduction always go hand-in-hand. Despite the name oxygen need not be present in an oxidation reaction. The substance that loses electrons is said to be oxidized the one that gains the electrons is said to be reduced.
A substance that loses electrons is said to be oxidized. The processes always occur simultaneously. Reduction is the gain of electrons by a substance.
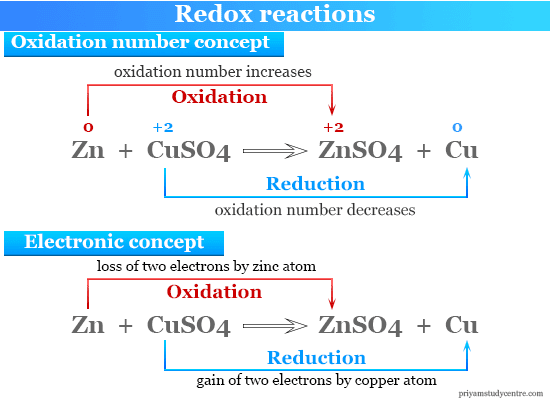
The redox reactions are very common and vital to the basic. An oxidation-reduction redox is a chemical reaction involving transfer of electrons between two species. The second reaction converts an oxidizing agent CuO into a reducing agent Cu.
Oxidation a loss of electrons and reduction a gain of electrons. During oxidation a substance loses one or more electrons. Oxygen gets reduced while iron gets oxidized.
Oxidation and Reduction. The opposite of oxidation is reduction. If you want tips on balancing redox equations see here.
The first reaction converts copper metal into CuO thereby transforming a reducing agent Cu into an oxidizing agent CuO. The opposite of oxidation is called reduction. If something is being oxidised something else must be being reduced.
The object of the. Redox reactions reactions in which theres a simultaneous transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another are really composed of two different reactions. During reduction a substance loses oxygen.
In reduction there is gain of electrons and the oxidation state of the molecules atoms or ions will be decreased. Reduction is gain of electrons loss of oxygen or gain or hydrogen. They certainly are when they balance a redox equation.
The electrons that are lost in the oxidation reaction are the same electrons that are gained in the reduction reaction. One substance is oxidized by the. Electrons are transferred from one reactant to another and the oxidation statesoxidation number of certain atoms are changed.
The reduced species receives electrons whereas the oxidised species loses them. 2 H 2 O 2 aq 2 H 2 O l O 2 g The key to this reaction lies in the oxidation states of oxygen however. The oxidized species loses electrons while the reduced species gains electrons.
During reduction a substance gains one or more electrons. Oxidation reduction is an exchange of electrons. An important feature of oxidation-reduction reactions can be recognized by examining what happens to the copper in this pair of reactions.
When electrons are gained by one substance the electrons must come from another. A reaction in which oxidation and reduction is occurring is called a redox. In H 2 O 2 oxygen has an oxidation state of -1.
Redox Reactions Definition Types Examples Application

Redox Oxidation Reduction Reaction Definition Examples
Oxidation And Reduction Reactions Basic Introduction Youtube
0 Comments